- Unity User Manual 2022.2
- 2D game development
- Physics 2D Reference
- 2D 关节
- Fixed Joint 2D
Fixed Joint 2D
Use the Fixed Joint 2D to connect two GameObjects controlled by Rigidbody 2D physics to keep them in a position relative to each other, so the GameObjects are always offset at a given position and angle. It is a spring-type 2D joint for which you don’t need to set maximum forces. You can set the spring to be rigid or soft.
Refer to Fixed Joint 2D and Relative Joint 2D for the differences between Fixed Joint 2D and Relative Joint 2D.
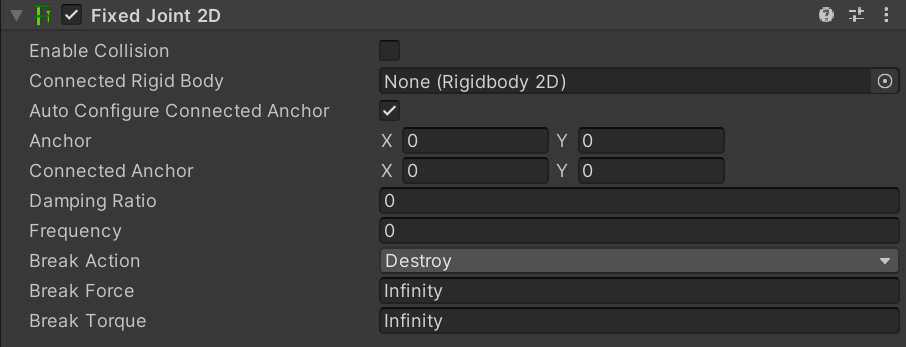
| 属性 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| Enable Collision | Enable this property to enable collisions between the two connected GameObjects. |
| Connected Rigid Body | Specify the other object this joint connects to. Leave this as None to have the other end of the joint fixed at a point in space defined by the Connected Anchor property. Select the circle icon to the right to view a list of GameObjects to connect to. |
| Auto Configure Connected Anchor | Enable this property to automatically set the anchor location for the other object this joint connects to. You do not need to enter coordinates for the Connected Anchor property if you enable this property. |
| Anchor | Define where (in terms of x, y-coordinates on the Rigidbody 2D) the end point of the joint connects to this GameObject. |
| Connected Anchor | Define where (in terms of x, y-coordinates on the Rigidbody 2D) the end point of the joint connects to the other GameObject. |
| Damping Ratio | Set the degree to suppress spring oscillation. In the range 0 to 1, the higher the value, the less movement. |
| Frequency | Set the frequency at which the spring oscillates while the GameObjects are approaching the separation distance you want (measured in cycles per second). In the range 0 to 1,000,000 - the higher the value, the stiffer the spring. Note: Setting Frequency to zero will create the stiffest spring type joint possible. |
| Break Action | Set the action taken when either the force or torque threshold is exceeded. |
| Break Force | Set the force threshold which if exceeded, will cause the joint to perform the selected Break Action. The default value is set to Infinity, which can never be exceeded and therefore the Break Action can never be taken while the threshold remains at this value. |
| Break Torque | Set the torque threshold which if exceeded, will cause the joint to perform the selected Break Action. The default value is set to Infinity, which can never be exceeded and therefore the Break Action can never be taken while the threshold remains at this value. |
Using this joint
The aim of this joint is to maintain a relative linear and angular offset between two points. Those two points can be two Rigidbody 2D components or a Rigidbody 2D component and a fixed position in the world. (Connect to a fixed position in the world by setting Connected Rigidbody to None).
线性偏移和角度偏移基于两个连接点的相对位置和方向,因此可以通过在 Scene 视图中移动连接的游戏对象来更改这些偏移。
The joint applies both linear and torque forces to connected Rigidbody 2D GameObjects. It uses a simulated spring that is pre-configured to be as stiff as the simulation can provide. You can change the spring’s value to make it weaker using the Frequency setting.
弹簧在游戏对象之间施力时,往往会超过对象之间的期望距离,然后反复反弹,导致连续振荡。阻尼比率决定了振荡减弱并使游戏对象停止的速度。频率是弹簧在目标距离任一侧进行振荡的速率;频率越高,弹簧刚度越大。
2D 固定关节同时有两个约束:
- 保持两个 2D 刚体游戏对象上的两个锚点之间的线性偏移。
- 保持两个 2D 刚体游戏对象上的两个锚点之间的角度偏移。
使用此关节构建的物理游戏对象就好像是通过刚性连接方式相连一样。游戏对象不能彼此远离,不能相互靠近,也不能相对于彼此旋转,例如桥梁的各个部分采用刚性连接。
还可以使用此关节来创建刚度稍低的柔性连接,例如桥梁的各个部分略带柔性。
Comparing Fixed and Relative joints 2D
了解 2D 固定关节与 2D 相对关节之间的主要区别是非常重要的:
- Fixed Joint 2D is a spring-type joint. Relative Joint 2D is a motor-type joint with a maximum force and/or torque.
- Fixed Joint 2D uses a spring to maintain the relative linear and angular offsets. Relative Joint 2D uses a motor. You can configure a joint’s spring or motor.
- Fixed Joint 2D works with anchor points (it’s derived from script Anchored Joint 2D); it maintains the relative linear and angular offset between the anchors. Relative Joint 2D doesn’t have anchor points (it’s derived directly from script Joint 2D).
- Fixed Joint 2D cannot modify the relative linear and angular offsets in real time. Relative Joint 2D can.
其他资源
- Refer to Joints 2D for more information about other 2D Joints.